five people in the middle of town Lincoln, New Hampshirehas been diagnosed with Legionnaires’ disease.
The New Hampshire Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) announced the news in an Aug. 12 press release.
It is likely that Five affected persons The release said the people came into contact with contaminated water droplets from a cooling tower behind the Riverwalk Resort, and tests confirmed the presence of Legionella bacteria in the water.
Health officials warn that a ‘Zika-like’ mosquito-borne virus has spread to Europe
“Anyone who has been in the area near a contaminated cooling tower should monitor themselves for symptoms,” New Hampshire State Epidemiologist Dr. Benjamin Chan said in the release.
“People who develop a fever or other symptoms of pneumonia within 14 days after spending time in this area should talk to their health care provider about getting tested for Legionella infection.”
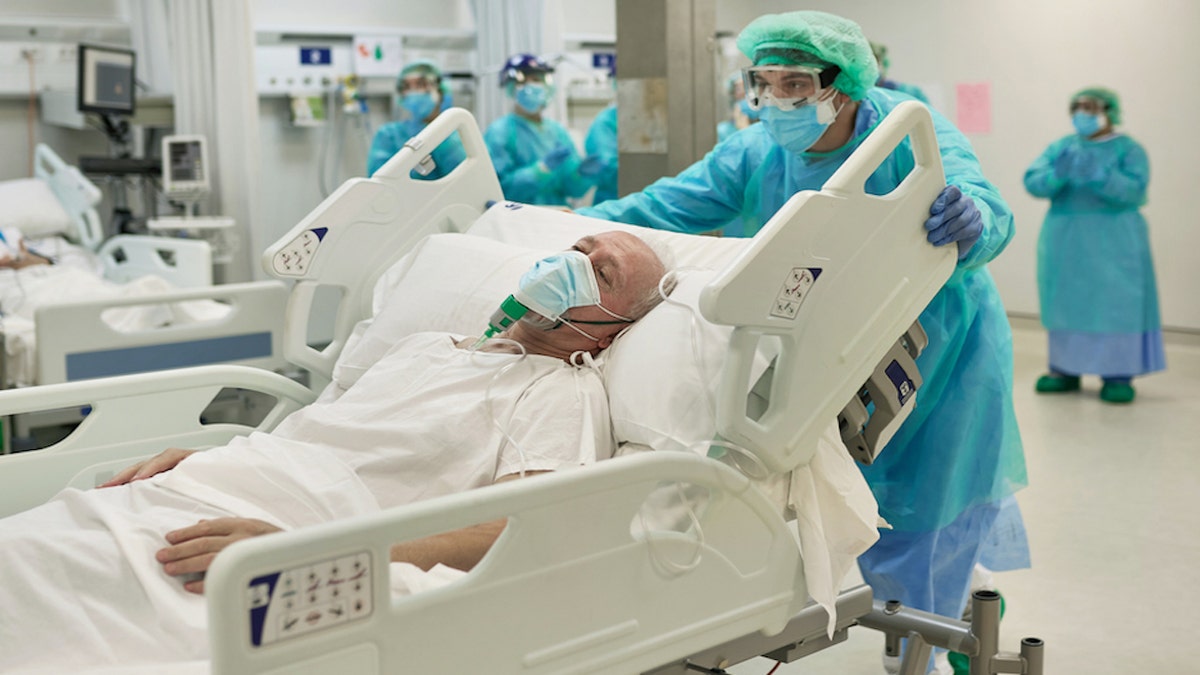
The CDC recommends that people who have certain symptoms — like those described in this article — should seek medical help immediately. (iStock)
DHHS warns that people within a half-mile of a cooling tower may also be at risk of exposure.
Cold, flu, COVID-19 and RSV: How to identify the different symptoms and stay safe
Fox News Digital has contacted DHHS for comment.
What is Legionnaires’ disease?
Legionnaires’ disease is a type of disease type of pneumonia Legionella is caused by bacteria.
This bacterium is commonly found in lakes, rivers, and other freshwater environments.
However, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), it can grow and spread indoors through shower heads, sink faucets, hot tubs, water features/fountains, plumbing systems, and other water systems.
When people swallow or breathe in water droplets containing Legionella, they can become sick with Legionnaires’ disease.
Although human transmission is possible in rare cases, the disease does not usually spread from person to person, according to the CDC.

Legionnaires’ disease is a type of pneumonia caused by Legionella bacteria. (iStock)
“Individuals most at risk include smokers and those with comorbid pulmonary disease,” Dr. Nathan Goodyear, medical director at Brio-Medical in Arizona, told Fox News Digital.
He added, “Other risk factors include increasing age, cardiovascular diseaseObesity and a weakened immune system.”
Signs of infection
Symptoms of Legionnaires’ disease usually appear between two and 14 days after infection.
Its symptoms are similar to those of other types of pneumonia, and include the following:
- cough
- Fever
- Difficulty in breathing
- Muscle aches and headaches
Some patients may also experience nausea, diarrhea and confusion, the CDC reported.
One doctor told Fox News Digital that individuals most at risk for Legionnaires’ disease include smokers as well as those with pulmonary disease. (iStock)
“The nature of the symptoms does not necessarily differentiate Legionella from other causes, but rather a history of contact with ‘man-made reservoirs,’ although this may be difficult to identify during an infection and/or outbreak,” Goodyear said.
“Cancer is also a co-morbidity of Legionnaires’ disease,” the doctor said.
People who have any of these symptoms Seek medical help The CDC recommends doing so immediately.
Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention
Legionnaires’ disease is diagnosed through a chest X-ray, urine test, and laboratory analysis of a sputum sample.
Most people with this disease recover with a course of antibiotics.
However, in some patients, severe illness can lead to lung failure or even death, according to the CDC.
Flu prevention tips from Florida’s surgeon general: ‘Everyday’ healthy lifestyle is key
According to the CDC, about 10% of people with Legionnaires’ disease die from these complications — and the risk of death increases by 25% for people who get Legionnaires’ disease while in a health care facility.
“Treatment must be prompt and aggressive,” Goodyear told Fox News Digital. “Legionella infection is an intracellular infection that requires treatment. antibiotic treatment,
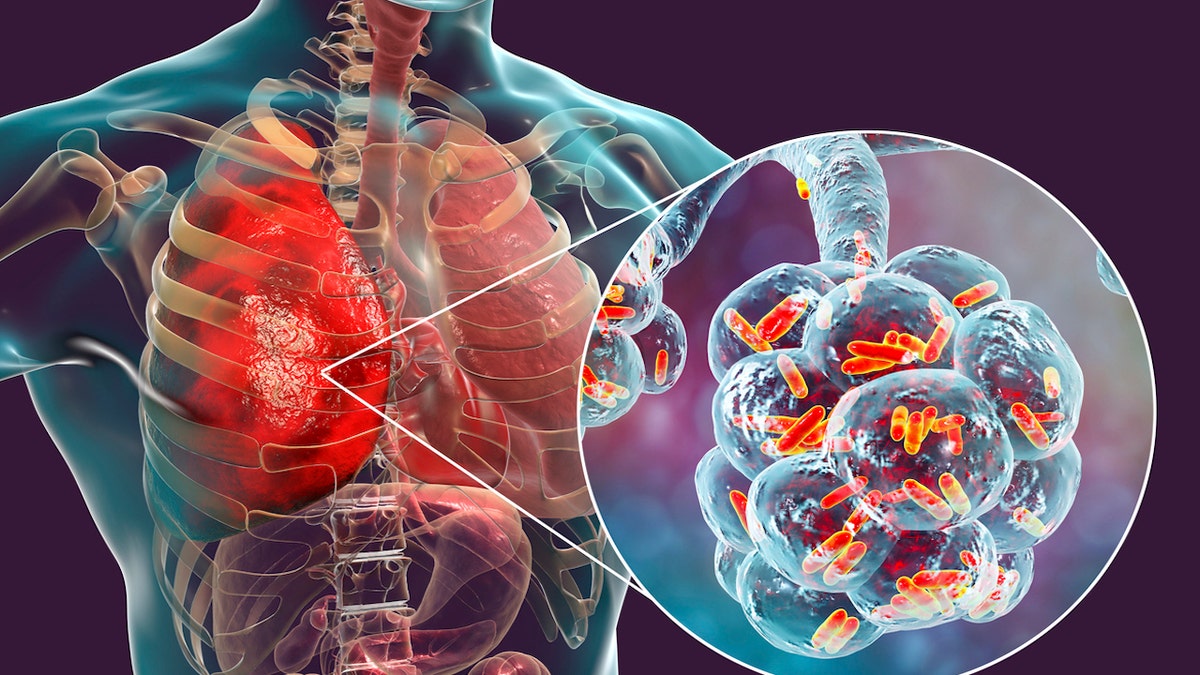
Legionnaires’ disease is diagnosed through a chest X-ray, urine test, and laboratory analysis of a sputum sample. (iStock)
Suitable antibiotics for Legionella infections include levofloxacin and azithromycin.
“In healthy individuals, therapy may be prescribed orally … but because of the pathogenesis of the disease, intravenous antibiotics often are the initial treatment option,” Goodyear said.
Click here to sign up for our health newsletter
Currently there is no vaccine available for this disease.
The best strategy to prevent infection is to reduce the growth and spread of Legionella bacteria.
The CDC recommends that building owners and managers use water management programs to reduce risk.

The CDC says the bacteria that causes Legionnaires’ disease can grow and spread through indoor water systems. (iStock)
To prevent severe Legionnaires’ disease, Goodyear recommends everyone: smokers should give up the habitThe study also emphasizes the need for “aggressive support” for chronic pulmonary disease.
For more health articles, visit here www.foxnews.com/health
“Aging is a certainty in life, and weakening of the immune system is associated with increasing age,” Goodyear said.
“Increasing immune support (vitamin D3, vitamin C, zinc) is essential to combat immune-related problems that come with aging.”
Click here to get the Fox News app
Obesity is another underlying risk factor for all chronic inflammatory diseases, Goodyear said.
















